microRNA Discovery: From 1992 to the 2024 Nobel Prize
by admin
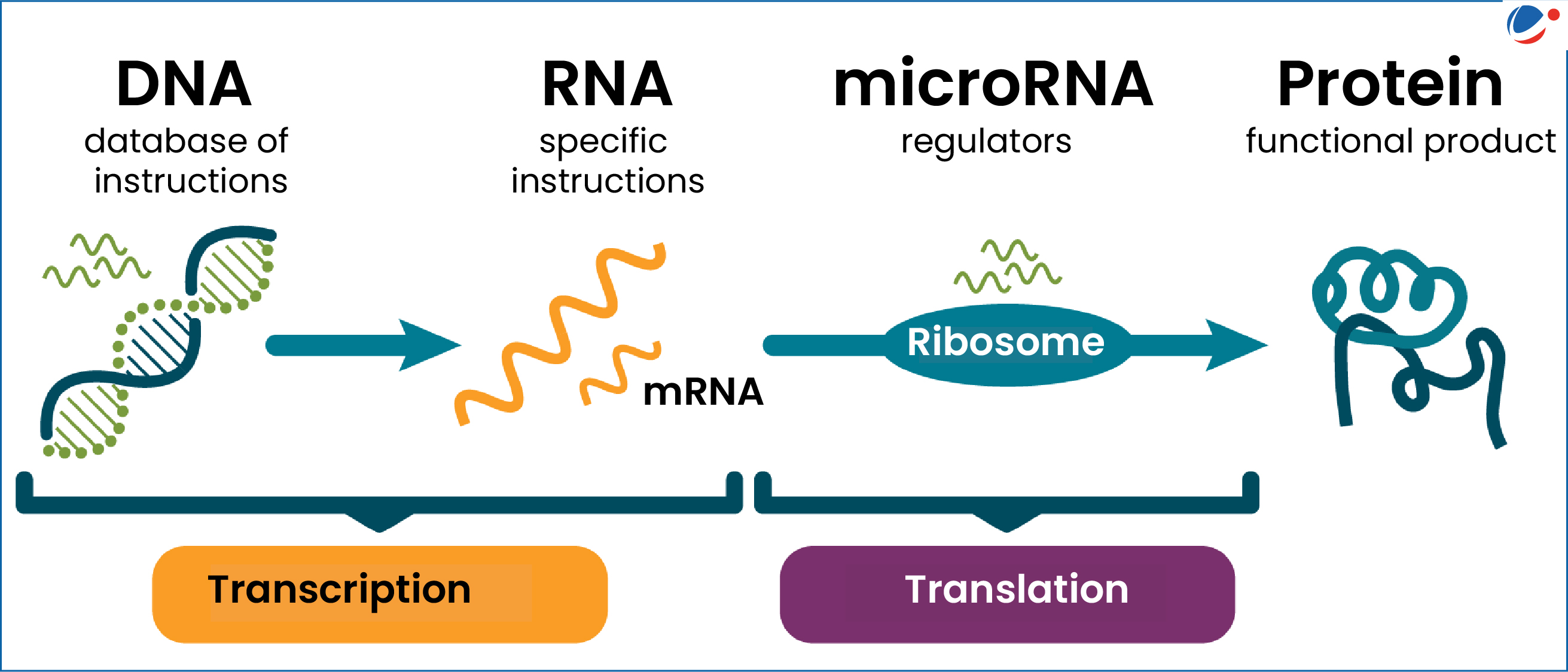
The discovery of microRNA in the early 1990s by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros marked a significant breakthrough in the field of gene regulation, ultimately earning them the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine in 2024. Their initial findings, which utilized the C. elegans model organism, revealed a new layer of complexity in genetic control, largely overlooked by the wider scientific community at the time. Funded primarily by NIH grants, their research began to gain traction as more scientists recognized the potential of microRNA in various biological processes. Today, the implications of microRNA research have expanded vastly, influencing areas such as cancer treatment and developmental biology. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of gene regulation, it becomes clear that microRNA is crucial for normal cellular function and presents exciting prospects for medical advancements.
MicroRNA research, a cutting-edge area in molecular biology, has opened doors to understanding the intricate mechanisms of gene expression. By investigating tiny RNA molecules, scientists are uncovering their critical roles in regulating genes and their expression in various organisms, including humans. The foundational work of researchers like Gary Ruvkun has catalyzed a surge of interest in RNA biology, drawing attention from multiple disciplines and spurring new therapeutic strategies. With significant backing from organizations like the National Institutes of Health, this field is rapidly evolving, revealing its importance in both health and disease. As we explore this fascinating realm, the impact of microRNA on biological systems continues to assert its relevance in modern science.
The Evolution of MicroRNA Discovery
The journey of microRNA discovery began in the early 1990s, primarily through the efforts of researchers like Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros. Initially, how they isolated and characterized microRNA in the model organism C. elegans did not seem revolutionary. The genetic community wasn’t fully aware of the potential biological significance of these tiny RNA fragments, leading to a lukewarm reception of their groundbreaking findings published in 1993. However, as research progressed, the pivotal role of microRNAs in gene regulation started attracting wider attention from diverse scientific fields.
Over the years, as more studies began to emerge, it became increasingly clear that the implications of microRNA research extended well beyond C. elegans. The realization that these small RNAs play fundamental roles in various organisms, up to and including humans, marked a significant turning point. Today, microRNAs are recognized as key regulatory elements influencing development, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis. This evolution from obscurity to a focus of intensive research symbolizes how groundbreaking discoveries can take time to be fully appreciated within the broader scientific community.
Federal Funding: A Catalyst for Scientific Growth
Gary Ruvkun emphasized the critical role of National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants in advancing his research on microRNA. For over 40 years, his laboratory relied significantly on federal funding, receiving approximately $150,000 annually, which was pivotal in establishing a sustainable research environment. This funding model allowed Ruvkun to create a dedicated team despite the lab’s relatively small size. It highlights a significant truth about scientific discovery: investment in basic research often leads to transformative breakthroughs that can alter our understanding of biology and medicine.
The steady financial support from federal agencies has not only facilitated the discovery of microRNAs but has also enabled the emergence of companies that leverage these scientific advances for developing therapeutic solutions. For instance, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, which specializes in RNA interference therapeutics, emerged from the foundational research funded by NIH grants. Ruvkun warns that a reduction in federal support may jeopardize the future of scientific innovation and exploration, with potential implications for the next generation of scientists who could find opportunities dwindling.
MicroRNA: Key Players in Gene Regulation
MicroRNAs have become essential players in gene regulation, influencing a myriad of biological processes. These small RNA molecules interact with target mRNAs to inhibit their translation or promote their degradation, thereby fine-tuning gene expression. The significance of microRNAs is apparent, as they are involved in critical life processes, including cellular differentiation, growth, and response to environmental stimuli. Advanced studies have established that almost a thousand microRNAs exist in the human genome alone, highlighting their ubiquitous role in regulating the majority of protein-coding genes.
The therapeutic potential of microRNAs in medicine is gaining momentum, with researchers investigating their roles in treating chronic diseases like cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate therapies that harness microRNAs, showcasing an exciting frontier in medical science. Thus, as our understanding of gene regulation evolves, the applications of microRNA research promise to revolutionize how we approach and treat some of today’s most challenging health issues.
Impact of Basic Research on Technological Advancements
The foundational research that Gary Ruvkun and his colleagues conducted on microRNAs has not only enhanced our understanding of genetic regulation but has also paved the way for significant technological advancements. Companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals owe their existence to the breadth of knowledge generated from NIH-funded basic research. This participatory relationship between basic research and technological innovation highlights the importance of investing in fundamental science, as it often leads to real-world applications and commercial breakthroughs that can drive economic growth.
Ruvkun firmly believes that a majority of thriving technology companies in the United States stem from research that received federal support. Federal grants have historically contributed to the development of transformative technologies, establishing the U.S. as a leader in scientific innovation. As global competition intensifies, continued investment in basic research will be crucial for maintaining technological superiority and addressing complex medical challenges facing society.
Global Recognition for MicroRNA Research
The recognition of microRNA research has escalated significantly since its inception, culminating in accolades such as the Nobel Prize awarded to Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in 2024. Their work on microRNA has not only influenced the field of genetics but has also reshaped our understanding of biological processes in multicellular organisms. As more scientists acknowledge the relevance of microRNAs to various fields, the global scientific community is increasingly collaborating to explore their applications in novel therapeutics.
Internationally, microRNA research has gained momentum, inspiring researchers around the globe to investigate its implications in developmental biology, cancer research, and regenerative medicine. The shift from a niche topic to a central theme in molecular biology signifies a broadening of perspectives, reminding the scientific community of the importance of innovative approaches in understanding life’s complexities. The increasing acknowledgment of microRNA’s role is paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries that transcend traditional boundaries in science.
The Future of MicroRNA Studies
Looking ahead, the future of microRNA studies promises to uncover even more intricate details about cellular functions and their implications in health and disease. As researchers continue to explore the diverse roles of microRNAs, they are likely to discover additional pathways and interactions that could influence therapeutic developments. Furthermore, advancements in genomic and bioinformatic technologies are providing scientists with more tools to investigate microRNA networks and their contributions to various biological processes.
As innovative research unfolds, the potential for microRNA applications in personalized medicine is becoming increasingly evident. MicroRNA profiles may one day serve as biomarkers, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, thus highlighting the relevance of ongoing funding and support for research endeavors. The quest to fully understand microRNAs will undoubtedly require collaboration across disciplines, ensuring that breakthroughs benefit diverse fields, including genetics, oncology, and pharmacology.
MicroRNA-Based Therapeutics on the Horizon
With the foundational discoveries of microRNA came the promise of innovative therapeutics tailored to address a spectrum of diseases. Current clinical trials focusing on microRNA-based treatments are already hinting at a future where these small molecules could lead to groundbreaking therapies for conditions like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Researchers are actively developing strategies to harness the regulatory power of microRNAs, aiming to either inhibit oncogenic microRNAs or restore the function of tumor suppressor microRNAs.
The success of microRNA-based therapeutics could signify a transformational shift in the treatment paradigm. As these therapeutic modalities advance through clinical trials, there is a growing anticipation of a future where gene regulation can be finely tuned to combat diseases that have traditionally posed great challenges. This exciting frontier underscores the critical need for continued support for research in this area, ensuring that the groundwork laid by pioneers like Ruvkun and Ambros propels us into a new era of medicine.
The Role of C. elegans in MicroRNA Research
The model organism C. elegans played a pivotal role in the discovery and understanding of microRNA. By utilizing this simple roundworm, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros made groundbreaking findings that laid the foundation for researching gene regulation through small RNAs. The simplicity of C. elegans allowed researchers to unravel the complex interactions of microRNAs and their target genes, providing insights that would eventually prove relevant to more complex organisms, including humans.
The unique attributes of C. elegans, such as its well-mapped genome and transparency during development, make it an invaluable tool for genetic research. As scientists continue to explore the implications of microRNAs, the C. elegans model will likely persist as a key player in elucidating the mechanisms of gene regulation, potentially offering solutions that address broader biological questions. This enduring relevance of C. elegans in microRNA studies symbolizes the importance of thoughtful selection of model organisms in advancing scientific knowledge.
The Importance of Grant Funding in Scientific Discovery
Gary Ruvkun’s experience exemplifies the essential role that federal grant funding plays in scientific discovery. For decades, his research has been primarily supported by NIH funding, which has allowed him to pursue groundbreaking studies in microRNA. This financial backing not only ensures the continuity of research but also inspires innovation among young scientists entering the field, proving that adequate resources are vital to nurturing future generations of researchers.
Without robust funding, the momentum in microRNA research could stall, limiting the potential for transformative discoveries. The allure of a scientific career must be sustained by stable funding sources to entice young talent into the field. Ruvkun’s cautionary words serve as a reminder that investment in basic research can yield immeasurable returns by catalyzing scientific advancements that have far-reaching impacts on both health and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of microRNA discovery in gene regulation?
The discovery of microRNA has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation. MicroRNAs play a crucial role in controlling gene expression by inhibiting the translation of messenger RNAs into proteins. This process is fundamental to organism development, maturation, and function, making microRNA research essential for understanding various biological processes and diseases.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to microRNA discovery?
Gary Ruvkun, along with Victor Ambros, made groundbreaking contributions to microRNA discovery in the early 1990s. Their research, primarily conducted using the C. elegans model organism, unveiled the role of microRNAs in regulating genes, which ultimately led to their recognition and award of the 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine.
What role did NIH funding play in microRNA research?
NIH funding has been instrumental in advancing microRNA research. For over 40 years, Gary Ruvkun’s lab has relied on federal grants, which supported foundational research that paved the way for significant breakthroughs in understanding gene regulation through microRNAs, ultimately linking this area of study to various diseases and therapeutic developments.
How are microRNAs relevant to human health?
MicroRNAs are integral to human health as they regulate most of the protein-producing genes in the human genome. Research has shown that about 1,000 microRNAs exist in humans, and therapeutic applications based on these small RNAs are in clinical trials for treating conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Why is the C. elegans model organism important in microRNA research?
The C. elegans model organism is vital for microRNA research due to its simplicity and well-mapped genetics. Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros utilized this model to make their initial discoveries about microRNAs in the early 1990s, providing foundational insights that have been applicable across different species, including humans.
What advancements have been made in microRNA applications in medicine?
Significant advancements have been made in the application of microRNA research in medicine. MicroRNAs are currently being explored as therapeutic agents for various diseases, with ongoing clinical trials focusing on their potential to treat conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders, showcasing their impact on modern medical treatments.
How has the perception of microRNA research changed since its discovery?
Since its discovery in 1992, the perception of microRNA research has evolved dramatically. Initially met with skepticism, interest in microRNAs has surged as their fundamental roles in gene regulation and implications for disease treatment have become clearer. The RNA field has expanded significantly, with growing recognition of microRNAs’ importance in biological research.
What challenges does microRNA research face in terms of funding?
Despite the critical importance of microRNA research, challenges remain in securing consistent funding. Researchers like Gary Ruvkun emphasize the need for ongoing NIH support, as reduced federal investment could impact the future of scientific inquiry and drive talented young scientists to seek opportunities abroad.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery Year | 1992-1993 |
| Discoverers | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros |
| Organism Studied | C. elegans (roundworm) |
| Significance | Revolutionary insights into gene regulation and development of microRNA as crucial molecules in gene expression. |
| Nobel Prize | Awarded in 2024 for contributions to microRNA research |
| Funding Source | Primarily from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) |
| Impact on Medicine | MicroRNAs are involved in therapies for diseases like heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s, currently in clinical trials. |
| Economic Influence | Contributed to the growth of companies like Alnylam, crucial for RNA therapeutic development. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery in the early 1990s marked a significant advancement in our understanding of gene regulation. Initially met with skepticism, the work by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros has evolved into a cornerstone of molecular biology, earning them a well-deserved Nobel Prize in 2024. Today, the role of microRNAs in regulating gene expression and their implications for therapeutic interventions in diseases such as cancer and neurological disorders are well recognized. This journey highlights the pathway from humble discoveries to groundbreaking scientific paradigms, showcasing the importance of sustained research funding and collaboration in driving innovation.
The discovery of microRNA in the early 1990s by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros marked a significant breakthrough in the field of gene regulation, ultimately earning them the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine in 2024.Their initial findings, which utilized the C.